[Coding028] Sort - 基数排序
Radix-sort
Get the knowledge flowing and circulating! :)
目录
标题:基数排序Radix-Sort Variation 1Radix-Sort Variation 2实例Radix-Sort Variation 3实例 (N = 10)拓展(Extensions)实例(Example)
标题:基数排序
Words & phrases
radix
美/ ˈreɪdɪks /
n.根;[数]基数
Radix sorting is widely used for its high efficiency.
基数排序由于其效率高而被广泛应用。
概念
基数排序(英语:Radix sort)是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较。
由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数。
实现方法
将所有待比较数值(正整数)统一为同样的数位长度(数位较短的数前面补零)。
然后,从最低位开始,依次进行一次排序。
这样从最低位排序一直到最高位排序完成以后,数列就变成一个有序序列。
基数排序的方式可以采用LSD(Least significant digital)或MSD(Most significant digital):
LSD:LSD的排序方式由键值的最右边开始;
MSD:与LSD相反,由键值的最左边开始。
——维基百科
Radix-Sort Variation 1
variation
美/ ˌveriˈeɪʃ(ə)n /
n.变化,变动;变奏曲;变化,变异;(天文)二均差;(数)变分,变差;磁偏角;(芭蕾)单人舞
Variation among humans is limited to the possible permutations of our genes.
人类的变化形式受限于我们基因可能的那些排列。
Uses bucket-sort as the stable sorting algorithm.
使用桶排序作为稳定排序算法。
Applicable to tuples where the keys in each dimension
适用于这样的元组,元组的键在每个维度上都是
runs in
运行时间复杂度为
Radix-Sort Variation 2
Consider a sequence of
考虑一个有
We represent each element as a
把每个元素表示为一个
runs in
时间复杂度为
sorts Java ints (32-bits) in linear time

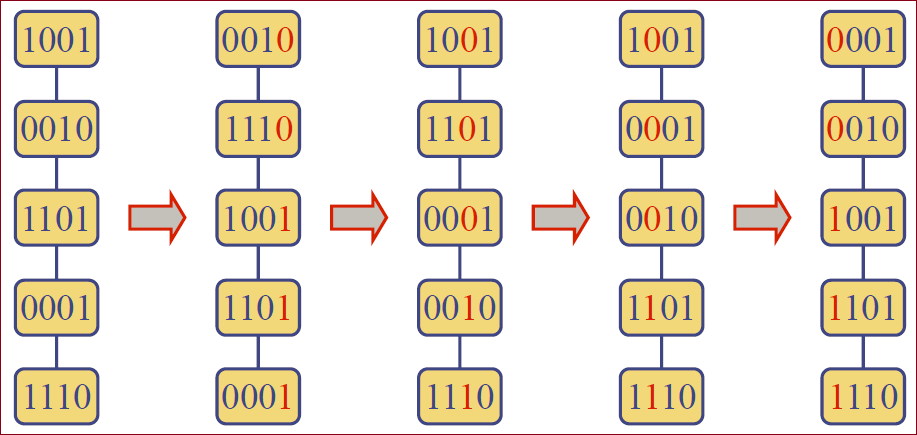
实例
(1001) (0010) (1101) (0001) (1110)
Sorting a sequence of 4-bit integers
Radix-Sort Variation 3
The keys are integers in the range
We represent a key as a 2-tuple of digits in the range [0, N − 1] and apply radish-sort i.e. we write it in base
现在考虑一下泛化情况(即,以N为基的radish-sort),十进制的整数就拆成多个十进制的单个数,例如75 →(7, 5)。
Example (N = 10):
75 → (7, 5)
十进制的数:
Example (N = 8):
35 → (4, 3)
八进制的数:
The running time is
运行时间复杂度为
Can be extended to integer keys in the range
实例 (N = 10)
keys are integers in the range [0, 99]
75, 12, 54, 33, 14, 87, 45, 17

拓展(Extensions)
Radix-sort string variation(适用于字符串的基数排序的变形)
The keys are strings of
每个键是包含
We represent each key by a
把每个字符串表示为一个
例如,字符串 “abc” 表示为 (1,2,3),因为a是第一个,b是第二个...
实例(Example)
Use the last variation to sort the following strings:
“cart ”, “core ”, “fore”, “cans”, “cars”, “bans”
